Growing Infertility in India
Infertility is a challenging and often emotionally taxing journey that affects millions of individuals and couples worldwide. Addressing this issue and seeking help at an early stage is crucial for those desiring to start or expand their families. Globally acknowledged organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have emphasized the significance of addressing infertility. Statistics reveal the widespread prevalence of infertility.
According to the WHO, approximately 9% of couples worldwide experience fertility problems. In the United States, the CDC reports that 12% of women aged 15-44 have difficulty getting pregnant or carrying a pregnancy to term. India is estimated to have one of the highest infertility rates in the world. It is reported that around 10-15% of couples in India struggle with infertility-related issues.
Infertility can result from a multitude of factors, including medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and age. The sooner individuals or couples acknowledge the issue and seek professional guidance, the better their chances of finding suitable treatments. This blog will delve into the various infertility treatment options available and provide valuable insights and guidance for those who may be grappling with this infertility issues.
Understanding Infertility: Causes and Categories
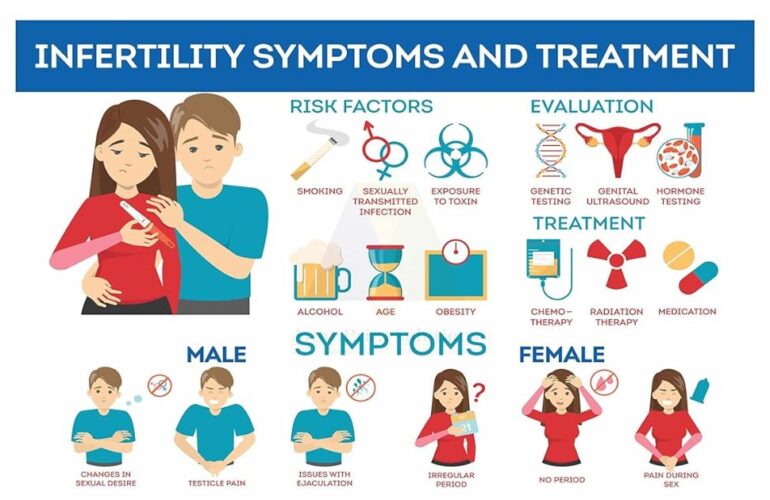
Infertility is a widespread concern affecting many individuals and couples across the globe, with India being no exception. To comprehend this issue, it is essential to define infertility, examine its various causes, and categorize it into male and female infertility. Let us delve into the details with reference to research from Indian and international journals.
Defining Infertility:
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular unprotected intercourse. In cases where a woman is above 35 years of age, this duration may be reduced to six months. International journals such as the “Human Reproduction Update” report a global infertility prevalence of approximately 9%. However, this figure can vary significantly by region and demographic factors.
- Male Infertility: Research published in the “Indian Journal of Urology” reports that male infertility accounts for approximately 50% of all infertility cases in India. Various factors contribute, including low sperm count, poor sperm motility, and structural abnormalities in the male reproductive system.
- Female Infertility: Female infertility can be attributed to several factors. A study in the “Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences” highlights those conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), blocked fallopian tubes, and age-related decline in egg quality are significant factors. Female infertility is estimated to contribute to 30-40% of infertility cases in India.
- Combined Causes: In some cases, both male and female factors can contribute to infertility. Research from the “Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences” indicates that in around 20% of cases, the cause is a combination of male and female infertility factors.
- Delayed Parenthood: Changing societal norms and delayed marriages because of career priorities have led to delayed parenthood. This trend contributes to an increase in age-related infertility.
According to a study published in the “Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences,” nearly 50% of infertility cases are due to male factors. Female factors contribute to about 30-40% of cases, and combined factors account for 20%. Research from the “Indian Journal of Psychiatry” underlines the emotional and psychological impact of infertility, revealing that up to 50% of infertile couples experience significant stress and anxiety. Understanding infertility and its multifaceted causes is the first step in addressing this issue.
Initial Steps and Diagnosis in Infertility
For couples facing fertility challenges, taking the right initial steps, and undergoing a proper diagnostic process is important. Understanding when to consult a fertility specialist and take diagnostic tests are key aspects in addressing infertility. Let us explore these steps and back them with relevant numbers and statistics, referencing a reputable source for clarity.
When to Consult a Fertility Specialist?
- Time Frame: If you have been actively trying to conceive for one year without success (or six months if the female partner is over 35), it is advisable to consult a fertility specialist.
- Age Consideration: Age plays a significant role in fertility. Women over 35 may consider consulting a specialist sooner due to the age-related decline in fertility.
Read About: Understanding Ovulation and Fertility
The Diagnostic Process:
- Medical History: The process begins with a comprehensive medical history assessment, where both partners’ health and reproductive histories are evaluated.
- Physical Examinations: Physical examinations are often conducted to identify any physical abnormalities in the reproductive system.
- Testing: Various tests and evaluations are employed to pinpoint the causes of infertility. These include:
- Hormonal tests to assess hormone levels and ovulation.
- Semen analysis to evaluate sperm count, motility, and morphology.
- Imaging tests, such as ultrasounds, to identify structural issues in the reproductive organs.
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG) to examine the fallopian tubes’ condition.
Consulting a fertility specialist and undergoing diagnostic tests are essential steps to uncover the underlying causes of infertility. With early intervention and tailored treatments, many couples can achieve their dream of parenthood.
Infertility Treatment Options in India
Infertility treatment options can be broadly categorized into four main approaches. Non-Invasive methods encompass lifestyle adjustments, medications, and carefully timed intercourse, providing fewer complex solutions for couples seeking to overcome fertility challenges. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART), including techniques like In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), offers advanced interventions for various infertility causes by fertilizing eggs and sperm outside the body.
Fertility Preservation is essential for individuals facing medical treatments that may compromise their future fertility, enabling them to freeze eggs or sperm. Finally, Surrogacy serves as a final solution when pregnancy is not possible due to medical conditions and that involves another woman carrying and delivering the child on behalf of the intended parents. These 4 options provide hope and tailored pathways to Infertile Couples in India.
1. Non-Invasive Infertility Treatment Options:
Non-invasive or less invasive infertility treatments offer hope and viable options for couples striving to overcome fertility challenges. These approaches often include lifestyle modifications, medications, and timed intercourse. Understanding their potential benefits and limitations is essential to making informed decisions.
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle adjustments can have a significant impact on fertility. Research indicates that simple modifications, like maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and minimizing alcohol consumption, can enhance fertility. For instance, a study published in the “Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology” noted that achieving a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI) significantly improved the chances of conception.
- Medications: Medications are frequently employed to address specific fertility issues. Ovulatory disorders, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can often be managed with medications. A review in the “Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews” revealed that ovulation-stimulating medications like clomiphene citrate led to a significantly higher pregnancy rate compared to a placebo.
- Timed Intercourse: Timed intercourse involves carefully tracking the woman’s menstrual cycle to pinpoint the fertile window when conception is most likely. Studies show that timed intercourse can substantially increase the chances of pregnancy. Research published in the “Human Reproduction” journal indicated that timed intercourse yielded a pregnancy rate of 38.3% in couples with unexplained infertility.
Benefits and Limitations: Non-invasive treatments are a less complex and more affordable starting point for couples. They carry fewer risks and may effectively resolve certain infertility issues. However, their effectiveness depends on the specific cause of infertility. Lifestyle changes, for instance, may not address structural or genetic factors. Medications can have side effects, and timed intercourse can be difficult to comply.
2. Assisted Reproductive Techniques:
Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART) are groundbreaking interventions that have revolutionized the field of fertility, offering hope to individuals and couples facing infertility. This category encompasses several sophisticated procedures, including Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), and the invaluable contributions of egg and sperm donation.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): IUI involves the careful selection and preparation of sperm, which is then placed directly into the woman’s uterus during her fertile window. It is a less invasive method, often used when male fertility factors are a concern. Success rates can vary but typically range from 10% to 20% per cycle.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a comprehensive and widely known ART procedure. It includes stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, retrieving these eggs, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory setting, and transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. The success rate for IVF varies depending on factors like age, but it typically ranges from 50% to 70% per cycle.
- Egg and Sperm Donation: Egg and sperm donation play pivotal roles in infertility treatments. Donor eggs are often used when a woman’s own eggs are not viable, while sperm donation addresses male infertility factors. These techniques offer hope to many couples. Success rates are promising, with around 50-80% live birth rates with donor eggs, and roughly 50% success with sperm donation, depending on various factors.
These assisted reproductive techniques have transformed countless lives by offering innovative solutions for a wide range of infertility causes. Understanding these options and meet a fertility Doctor in Noida for Consultation.
3. Fertility Preservation:
Fertility preservation, an increasingly vital aspect of reproductive medicine, offers individuals the opportunity to safeguard their reproductive potential. One of the most prominent methods in this category is egg freezing, which can be a lifeline for those facing medical treatments or life circumstances that could compromise their fertility.
- Egg Freezing: Egg Freezing is an innovative technique where a woman’s eggs are harvested, frozen, and stored for future use. This method is particularly beneficial for females facing medical treatments such as chemotherapy. It is also an option for those who wish to delay parenthood due to career or personal reasons.
- Sperm Freezing: Sperm freezing, or cryopreservation, is a method of preserving sperm samples at very low temperatures. Sperm can remain viable for years when frozen, with a success rate of about 50% to 80% for fertilization. It is often used by men facing medical treatments, like chemotherapy.
- Embryo Freezing: Embryo freezing, a part of assisted reproductive technology, involves preserving embryos created during IVF. These embryos are cryogenically stored for later use. It provides flexibility and increased chances of conception for couples who have undergone IVF or wish to postpone pregnancy.
When to Consider Fertility Preservation:
- Medical Treatments: Patients undergoing treatments like cancer therapies that may harm reproductive organs or hormonal function should explore fertility preservation options before commencing treatment.
- Delayed Parenthood: As societal norms evolve and individuals prioritize education and career, many are delaying parenthood. Egg freezing can be a wise choice for women who want to preserve their fertility as they age.
- Genetic Conditions: Individuals with genetic conditions that may lead to early fertility loss should consider fertility preservation.
- Family Planning: Fertility preservation can also be an option for those who want to ensure their ability to have children in the future but are not ready for parenthood presently.
Reference to Indian Medical Guidelines: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has provided comprehensive guidelines on fertility preservation. These guidelines emphasize the importance of informing patients about fertility preservation options before medical treatments that can affect fertility and ensuring ethical and effective practices in this field. These guidelines offer valuable direction and support for both Fertility Clinics and patients.
4. SURROGACY:
As per the Surrogacy (Regulation) Act of 2021, surrogacy is available to a widow or divorcee aged 35 to 45, or a legally married couple, provided they have a medical condition that requires this reproductive option To opt for surrogacy in India, you must be a legally married Indian couple, with the man aged between 26-55 and the woman between 25-50. You should not have prior biological, adopted, or surrogate children. The law strictly prohibits commercial surrogacy, carrying penalties of up to 10 years in jail and fines of Rs 10 lakhs.
The law permits only selfless surrogacy, which implies that the surrogate mother is not allowed to receive any form of compensation beyond covering the medical expenses incurred during pregnancy, including insurance coverage. Any form of commercial surrogacy, where compensation is provided to the surrogate in cash or in-kind, is prohibited. Before the prospective couple can proceed with the surrogacy process, they must acquire two certificates – a certificate of necessity and a certificate of eligibility – from an authorized body. To obtain a certificate of necessity, specific conditions must be met. The couple is required to present a certificate from a District Medical Board, confirming their infertility and their inability to conceive.
FAQ’s
Q1. What are 2 options for infertility?
Two widely employed fertility treatments include:
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): This procedure involves the direct insertion of healthy sperm into the uterus during the ovulation phase, facilitating the fertilization process.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF encompasses the retrieval of eggs from the ovaries, their fertilization with sperm within a laboratory setting, leading to the development of embryos, which are later transferred into the uterus.
Q2. What is the most popular fertility treatment?
Broadly, IVF stands out as the most potent and effective treatment for a wide spectrum of infertility conditions, encompassing age-related and unexplained cases.
Q3. What is usually the first treatment for infertility?
Typical fertility medications comprise Clomiphene Citrate, Letrozole and gonadotropins. However, one must Consult a Fertility Doctor as these medications cannot be self-prescribed.
Q4. How can I get pregnant without IVF?
Two approaches to stimulate ovulation and address infertility are the following:
- Ovulation-Inducing Medications: There are numerous medications designed to trigger ovulation like Clomiphene Citrate, Aromatase Inhibitors, such as Letrozole, Metformin and Gonadotropins
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI).
Q5. What are the 3 types of IVF?
There are three primary IVF approaches that use minimal or no medications: natural cycle IVF, gentle stimulation IVF, and in vitro maturation (IVM).
Q6. How can I check my fertility?
This requires the Assessment of Egg Quality, Uterus, and Fallopian Tubes. In the evaluation process an ultrasound imaging is done to examine your ovaries and uterus, along with conducting hormone level tests through a blood sample. Additionally, you might be advised to initiate monitoring of your ovulation patterns, which can involve observing changes in cervical mucus, recording basal body temperature, or utilizing home-based ovulation tests.
Q7. Are there fertility pills?
Fertility drugs are used when natural pregnancy efforts fail. These are primarily prescribed for women with polycystic ovary syndrome and individuals with hormone imbalances. These Pills are Clomiphene Citrate, Letrozole, Metformin and Gonadotropins.
Q8. Which fertility treatment has the highest success rate?
IVF boasts the most favorable success rates when compared to other fertility treatments. This assisted reproductive technology is a comprehensive solution for a wide spectrum of fertility challenges. IVF effectively addresses both male and female infertility by facilitating fertilization in a laboratory setting and subsequently transferring the embryo into the uterus for successful implantation. When performed by a skilled specialist at the appropriate age, IVF can achieve a remarkable success rate, with some cases reaching as high as 90%.
Q9. Why is IVF not 100% successful?
Couples should be aware that the success of IVF is influenced by several factors. These factors include the woman’s age, the health of her uterus, the quantity and quality of viable eggs, the quality of the man’s sperm, as well as various biological and hormonal factors.
Q10. What is the age limit for IVF?
According to the recently enacted Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) (Regulation) Act of 2021 in India, there is a strict age limit for IVF procedures. This law sets the maximum age at 50 years for women and 55 years for men to undergo assisted reproductive technology treatments.
Q11. What is the cost of IUI treatment?
IUI treatment expenses in India can vary, typically ranging from Rs. 15,000 to Rs. 20,000 INR. The overall cost can be influenced by factors like age, the number of cycles, medications, and the chosen clinic and doctor’s expertise.
Q12. What is the average cost of IVF?
Based on our findings, the average expenditure for IVF treatment in India is approximately 1.5 lakh INR.
Q13. Is IUI is painful?
IUI is a simple procedure that does not necessitate pain medication or anesthesia. Patients may feel a minor pinch (like a routine pap smear) and some mild cramping when the catheter is inserted through the cervix.