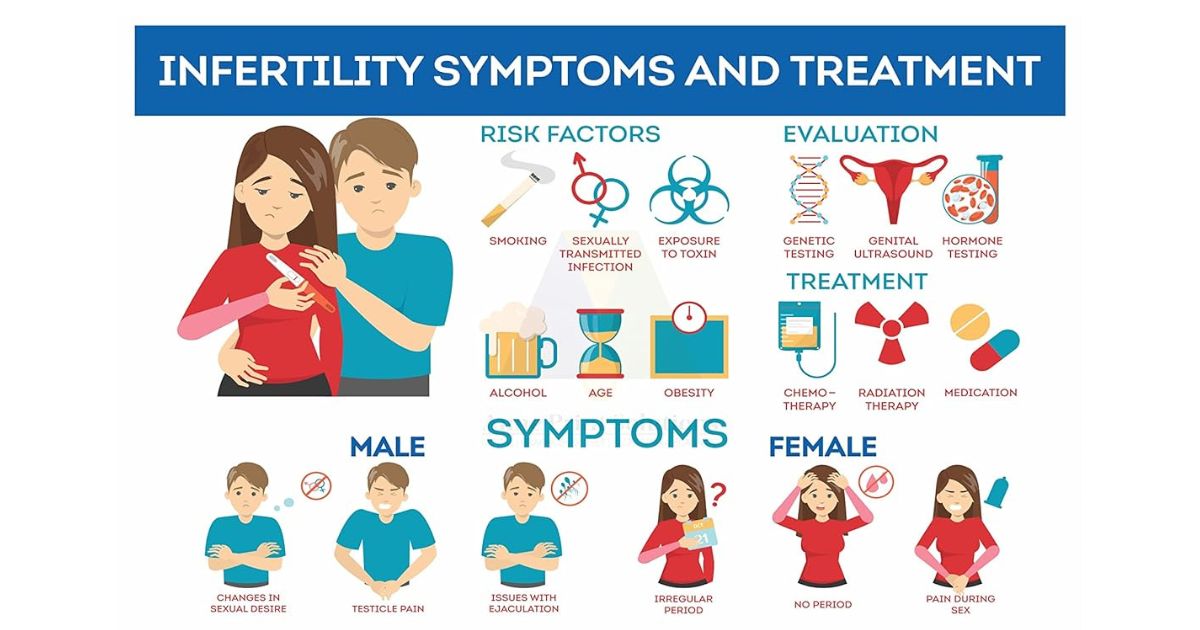
Infertility is medically defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes infertility as a global public health issue. In India, studies published in the International Journal of Fertility & Sterility indicate that infertility affects nearly 10-14% of the Indian population, with higher rates in urban areas due to lifestyle factors.
Understanding infertility requires a basic knowledge of the reproductive systems. In females, it involves a complex cycle of hormone regulation that prepares the ovary to release an egg and the uterus to receive a fertilized egg for implantation. Male infertility, on the other hand revolves around the quantity and quality of sperm production. Issues such as low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormalities in sperm function impede the natural fertilization process.
Common misconceptions about infertility include the belief that it is only a woman’s issue. Male infertility contributes to around one-third of infertility cases according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Another myth is the assumption that young couples are less likely to experience infertility. This is refuted by clinical evidence demonstrating that age-independent factors such as environmental toxins, stress, and lifestyle choices can affect fertility.
Recognizing signs and symptoms early can be crucial. For women, irregular menstrual cycles, severe menstrual cramps, or a history of miscarriages can be early indicators. In men, changes in sexual function or testicular pain can be signs. The importance of early recognition lies in the wider range of treatment options available at earlier stages and the possibility of addressing reversible causes.
Signs And Symptoms of Infertility in Women
Infertility in women can manifest through various signs and symptoms, affecting their reproductive health. These indicators can be early warning signs of underlying fertility issues.
1. Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
- Irregular menstrual cycles, where the length and regularity vary significantly, can be a sign of hormonal imbalances or ovulatory disorders.
- Around 30-40% of infertility cases in women are attributed to irregular periods according to the American Pregnancy Association.
2. Painful or Heavy Periods:
- Painful periods, or dysmenorrhea, can result from conditions like endometriosis or uterine fibroids.
- Approximately 30-40% of women with endometriosis experience infertility, as reported by the World Endometriosis Society.
3. No Periods (Amenorrhea) or Light Periods:
- Amenorrhea, the absence of menstruation, can be due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hypothalamic amenorrhea.
- PCOS affects up to 10% of women of childbearing age and is a leading cause of infertility.
4. Symptoms of Hormone Fluctuations:
Hormonal fluctuations are the leading cause for the following symptoms.
- Skin Changes: Conditions like acne or excessive facial hair growth (hirsutism) may indicate hormonal imbalances.
- Weight Gain: Sudden and unexplained weight gain can be linked to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders.
- Reduced Sex Drive: Changes in libido can result from hormonal imbalances or psychological stress.
- Thinning Hair or Hair Loss: Androgenic alopecia is often related to hormonal imbalances.
- Other Hormonal Imbalance Indicators: Mood swings, fatigue, and changes in breast size can also occur.
5. Pain During Sex:
- Pain during intercourse can be associated with endometriosis, uterine fibroids, or other gynecological conditions.
- Approximately 10-40% of women with endometriosis report experiencing pain during sex, as per the American Society for Reproductive Medicine.
One must note that these symptoms are not exclusive to infertility and can be also the signs for other medical conditions. However, couples facing difficulty in conceiving, these signs can indicate an underlying fertility issue.
Common Causes Linked to Infertility Symptoms
Addressing infertility requires an understanding of its multifaceted causes. In India, where cultural importance is placed on procreation, infertility carries significant social implications. Below is a list of 6 common causes of infertility with relevant data from Indian studies and popular references.
1.Ovulation Disorders: Ovulation disorders account for infertility in a substantial portion of couples. According to a study published in the Journal of Human Reproductive Sciences, they are responsible for around 18-25% of infertility cases in India. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is particularly prevalent, affecting approximately 9.13% to 36% of women of reproductive age in India, as per a report in the Indian Journal of Medical Research.
2.Tubal Occlusion: Tubal factor infertility is a significant issue, accounting for approximately 25-30% of infertility cases in India, according to the All-India Institute of Medical Sciences. Pelvic inflammatory disease, often a consequence of sexually transmitted infections, is a common cause.
3.Uterine or Cervical Abnormalities: Uterine anomalies are implicated in 2-5% of infertile women, while cervical factors contribute to about 5% of infertility cases, as noted in various studies across Indian populations.
4.Endometriosis: Endometriosis is found in 20-30% of women who are infertile, which is consistent with international statistics. Indian Journal of Medical Research reports that it affects roughly 25% of women experiencing infertility.
5.Male Factor Infertility: Male infertility is a significant and growing issue, with an estimated contribution to 40-50% of all infertility cases in India, according to a study published in the International Journal of Infertility & Fetal Medicine. Conditions like varicocele are found in 19.3% of men attending infertility clinics as per the Indian Journal of Urology.
6.Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, which affects 135 million individuals in India according to The Lancet, has been linked with infertility. Smoking, which has a prevalence of about 9% among Indian women as per the Global Adult Tobacco Survey, and higher in men, has been correlated with fertility issues. Alcohol consumption, although lower in India compared to Western countries, is on the rise and its impact on fertility is becoming more evident.
References for more detailed statistics:
- Prevalence of polycystic ovary syndrome in Indian adolescents: – The Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.
- Prevalence of Male Factor Infertility in India: A Systematic Review in the International Journal of Infertility & Fetal Medicine.
- Global Adult Tobacco Survey (GATS) India Report.
- The changing patterns of hypertension, obesity, and diabetes in India in The Lancet.
These publications can provide further detailed statistics and are available for deeper insight into the prevalence and causes of infertility within the Indian context.
Read About: Infertility Treatment Options in India
When To See a Doctor for Infertility
Addressing infertility often requires timely action and an informed approach. I have highlighted a simple and structured to explore when to seek medical assistance, the significance of both partners undergoing testing, and what to anticipate during a fertility evaluation. The importance of early intervention makes all the difference.
- Recommended Timelines for Seeking Help: Seeking medical assistance for infertility is crucial, but the right timing can vary. In general, couples under 35 years old who have been trying to conceive for a year without success should consider seeking help. However, if a woman is over 35, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider after six months of unsuccessful attempts. These timelines are derived from research by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Delaying consultation can affect treatment options, as female fertility declines with age.
- The Importance of Both Partners Getting Tested: Infertility is not solely a female issue. Male factor infertility contributes to a significant portion of cases, with around 40-50% attributed to male factors. A study published in the International Journal of Infertility & Fetal Medicine highlights the increasing prevalence of male infertility in India. Therefore, both partners should undergo testing to identify the root causes of infertility. Ignoring one partner’s health can result in misdiagnosis or the delay of appropriate treatment.
- What to Expect During a Fertility Evaluation: During a fertility evaluation, both partners can expect a series of assessments to determine the cause of infertility. This may include a review of medical history, a physical examination, and various tests. For women, these tests may involve assessing hormone levels, ovulation, and the condition of the reproductive organs through ultrasounds. In men, semen analysis is a critical component. The results of these evaluations guide fertility doctors in formulating a treatment plan.
Diagnosis And Testing for Infertility
The diagnosis and testing of infertility involve a series of assessments to identify the underlying causes of fertility issues. The process typically includes initial assessments, lab tests, imaging tests, and specialized examinations. We have shared each of these components and approximate costs in Indian Rupees (INR).
- Initial Assessments and Physical Examinations: The initial step in diagnosing infertility involves a comprehensive medical history review and physical examination. These assessments aim to identify any potential issues or lifestyle factors that may be contributing to infertility. The cost of these initial assessments varies, but it can range from 1,000 to 2,000 INR, depending on the Infertility Clinics in India.
- Lab Tests (Hormone Testing, Semen Analysis, etc.): Lab tests are crucial in the fertility evaluation process. Hormone testing, which can include assessing levels of FSH, LH, estradiol, and thyroid hormones, costs around 2,000 to 4,000 INR. Semen analysis, a key test for male factor infertility, ranges from 1,500 to 3,000 INR.
- Imaging Tests (Ultrasounds, Hysterosalpingography, etc.): Imaging tests provide insights into the condition of reproductive organs. Transvaginal ultrasounds can cost between 1,500 and 3,500 INR. Hysterosalpingography, which examines the fallopian tubes and the uterine cavity, typically ranges from 4,000 to 6,000 INR. The cost can vary based on various IVF Clinics in India.
- Specialized Tests (Laparoscopy, Genetic Testing, etc.): Specialized tests are employed when other assessments do not yield a clear diagnosis. Laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure to examine the abdominal and pelvic organs, may range from 20,000 to 50,000 INR, depending on the complexity. Genetic testing, which can identify chromosomal or genetic factors contributing to infertility, varies in cost depending on the specific tests and ranges from 5,000 to 15,000 INR or more.
Please note that these cost estimates are approximate and can vary significantly based on the IVF center in India and specific tests required. The total cost of infertility testing may accumulate, and it is advisable to discuss expenses with a financial counsellor in the clinics that you contact.
Treatment Overview of Infertility
The treatment of infertility often involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle adjustments, medications, surgical interventions, and assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Each treatment avenue aims to address specific underlying causes and comes with varying costs, particularly relevant in the Indian healthcare context.
- Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies: For many couples, lifestyle modifications can significantly enhance fertility prospects. These changes include adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption. There is no direct cost associated with lifestyle changes except for possible expenses related to nutrition counseling or a gym membership, which can range from 500 to 5,000 INR per month.
- Medications to Enhance Fertility: Fertility drugs are often the first treatment option. For women, medications such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole, which stimulate ovulation, can cost approximately 500 to 2,500 INR per cycle. Gonadotropins are more expensive, ranging from 5,000 to 20,000 INR per cycle. For men, medication to improve sperm count and quality may also be prescribed, with costs varying by drug and dosage.
- Surgical Options: Surgery may be required to correct issues like endometriosis, uterine problems, or blocked fallopian tubes. Costs for surgical treatment of infertility can be substantial, ranging from 30,000 to 200,000 INR depending on the complexity and type of surgery performed.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) such as IVF: ART is often considered when other treatments have failed. In vitro fertilization (IVF), the most well-known form of ART, involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and implanting it in the uterus. The cost for one cycle of IVF in India varies widely from 1 lakh to 2 lakhs INR depending on the number of cycles and additional procedures like Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) or preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD). Other ART procedures include intrauterine insemination (IUI), which is less expensive than IVF and can cost between 10,000 to 20,000 INR per cycle.
Coping With Infertility
- Psychological Impact of Infertility: Infertility can have a profound emotional toll on individuals and couples. It often leads to feelings of frustration, guilt, anxiety, and depression. Coping with these psychological challenges is an essential aspect of infertility treatment.
- Support Groups and Counseling: Support groups and counseling provide invaluable emotional and psychological support for individuals and couples facing infertility. These resources offer a safe space to share experiences and strategies for managing the emotional burden of infertility.
- Considering Alternatives (Adoption, Surrogacy): Exploring alternatives like adoption or surrogacy is an essential part of coping with infertility. Dr. Mona Dahiya is considered a trusted advisor for patients in this journey. Her expertise and compassionate counseling help patients make informed choices, alleviating the stress associated with such decisions. Dr. Dahiya’s guidance is instrumental in helping individuals and couples navigate the complex landscape of infertility, offering hope, and providing support as they explore alternative paths to parenthood. Her holistic approach goes beyond medical treatment, addressing the emotional and psychological dimensions of infertility.
FAQ’S
Q1. What are the causes and treatment of infertility?
Infertility occurs when pregnancy remains elusive after a year of trying. It may stem from issues like irregular ovulation, endometriosis, low sperm count, or hormonal imbalances. Age can heighten the risk of infertility. Fortunately, numerous treatments exist to address these challenges.
Q2. What is the main symptom of infertility?
Infertility primarily presents as difficulty conceiving. Irregular, absent, or very long/short menstrual cycles often signal a lack of ovulation, typically without additional symptoms.
Q3. What are the 4 causes for female infertility?
- Ovulation disorders, such as PCOS, impacting egg release.
- Tubal blockage or damage preventing egg-sperm meeting.
- Uterine conditions, like fibroids, affecting embryo implantation.
- Endometriosis, where tissue grows outside the uterus.
Q4. What are the 6 causes of infertility?
- A woman’s age: Advanced maternal age can significantly impact a woman’s fertility as the quality and quantity of eggs decline with age.
- Male (sperm) factor: Male infertility due to low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm morphology can impede conception.
- Ovulation disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation, often associated with conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can lead to infertility.
- Tubal disease: Blockages or damage to the fallopian tubes can obstruct the passage of eggs and sperm, making fertilization difficult.
- Endometriosis: The presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus can cause inflammation, scarring, and structural changes in the reproductive organs, affecting fertility.
- Anatomical factors such as fibroids and other uterine abnormalities: Uterine conditions like fibroids can disrupt the implantation of a fertilized embryo and the overall reproductive process.
Q5. What is the best treatment for infertility?
IVF is hailed as the leading treatment for infertility due to its high success rates which vary depending on various factors but can average around 40% per cycle. IVF has helped over 8 million babies have been born since the first case in 1978. This technique is particularly effective for those with fallopian tube issues, severe male infertility and unexplained infertility.
Q6. How can I check my fertility at home?
Many at-home fertility tests are available these days. These include ovulation prediction kits, FSH tests, and semen analysis kits. Costs and precision of these tests vary and one must consult a fertility doctor for guidance.
Q7. Can infertility be cured?
Fertility treatment is highly individualized depending on primarily age and individual health factors. Hence there is no universal solution for infertility but tailored approaches like medications, IUI, IVF and lifestyle Changes are proven ways to cure infertility.
Q8. When do signs of infertility start?
The primary indicator of infertility is the inability to conceive after six months to one year of consistent, unprotected sexual activity. While many may not exhibit additional symptoms, some individuals might experience physical signs, like pelvic or abdominal discomfort.
Q9. Why my wife is not getting pregnant?
Occasionally, women may have irregular ovulation, where the ovaries do not release eggs consistently. Signs such as rare or absent menstrual cycles could indicate conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hormonal imbalances, stress, or being underweight. Excess weight can also cause issues with ovulation, as can abnormalities in the uterus.
Q10. Who are at risk of infertility?
Female fertility gradually decreases with age, particularly from the mid-30s onward, and this decline accelerates after the age of 37. Reduced fertility in older women often results from a combination of diminished egg quantity and quality, along with potential health issues impacting reproductive abilities. It is worth noting that men aged 40 and above may also experience decreased fertility compared to younger men.
Q11. Can masturbation cause low sperm count?
Regular male masturbation is unlikely to significantly impact fertility. Some studies indicate that the best semen quality occurs after abstaining from ejaculation for two to three days. However, other research suggests that men with normal sperm quality can maintain their sperm motility and concentrations even with daily ejaculation.
Q12. What is the first treatment for infertility?
For unexplained infertility, the initial recommended treatment is often 100mg of Clomiphene citrate combined with intrauterine insemination (IUI).
Q13. What foods increase fertility in woman?
Go for plant-based foods, like whole fruits such as apples, bananas, oranges, strawberries, raspberries, mangos, guava, and the fertility-boosting pineapple. These options are rich in fiber and essential vitamins. Include seasonal vegetables in your diet as well.
Q14. How do I start a fertility treatment?
Consult with an Infertility Doctor near you. You can take suggestions from a known obstetrician or a Gynaecologist who can recommend a known as a reproductive endocrinologist or IVF Doctor.
Q15. Can I check if I am infertile?
If you suspect infertility issues in yourself or your partner, try and get assessed by a doctor who specializes in reproductive medicine. The initial stages usually encompass a doctor’s consultation, Blood Tests, Pelvic ultrasound, and an analysis of semen.
Q16. Can I get pregnant if my husband is infertile?
Is conception possible despite male infertility? Yes, if a man generates some sperm, there remains a potential for pregnancy. In fact, couples facing challenges like low sperm counts or abnormal sperm have in some cases achieved conception without the need for additional interventions.
Q17. What are the symptoms of poor egg quality?
Symptoms like infertility, recurrent miscarriages, and irregular menstrual cycles can be indicative of diminished egg quality. With advancing age, women may experience a decline in egg quality, which can lead to chromosomal abnormalities that impact the success of pregnancy.
Q18. What is a normal sperm count to get pregnant?
A healthy sperm count typically varies from 15 million to over 200 million sperm per milliliter of semen. Counts below 15 million sperm per milliliter or less than 39 million sperm in total per ejaculation are classified as low.
Q19. Does female masturbation increase fertility?
The answer is NO. Masturbation and achieving orgasm do not influence women’s ovulation or fertility. To dispel any concerns regarding the link between masturbation and ovulation, you can monitor your ovulation cycle to witness this independently.
Q20. At what age is egg quality best?
A woman’s best years for reproduction are typically from her late teens to her late 20s. Fertility begins to wane when she hits 30 and accelerates after mid-30s. By 45, chances of conceiving naturally are significantly reduced due to the considerable decrease in fertility.
Q21. How can I test my husband’s sperm?
Using self-test kits at home, you can gather a semen sample and perform a sperm count independently. Certain kits even incorporate a smartphone-compatible device to assess sperm motility and concentration in the semen. Alternatively, self-collection kits allow you to collect a semen sample at home and send it to a laboratory for analysis.
Q22. Which fruit will increase sperm count?
Bananas, apples, pomegranates, avocados, and dark berries are top fruits loaded with vital nutrients that may boost fertility and enhance sperm quality.
Q23. How can I improve my egg quality fast?
Exercise, yoga, and staying active can enhance blood circulation to the ovaries, potentially improving egg health. Keeping hydrated by drinking plenty of water may also support detoxification and overall reproductive health.
Q24. What are most common causes of Female infertility?
Infertility is often linked to issues with ovulation, the most prevalent cause in women. Factors like age, hormonal imbalances, excessive weight and smoking can significantly influence a woman’s fertility.
Q25. How can I increase my fertility?
- Adopt Healthy eating patterns.
- Exercise to Keep weight within healthy BMI range.
- Consume a folate-inclusive multivitamin.
- Cut down on caffeine.
- Steer clear of alcohol & Smoking.
- Practice Meditation to Combat Stress.
About Dr. Mona Dahiya
Dr. Mona Dahiya is widely recognized as one of India’s top infertility doctors. She has a remarkable 25-year career experience and has helped over 5000 couples fulfill their dreams of parenthood. With a solid educational foundation, she earned her MBBS from the prestigious Lady Hardinge Medical College in Delhi, followed by an MD from Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi. Her commitment to excellence and a deep passion for her field led her to acquire a Fellowship from the Singapore General Hospital.
Dr. Dahiya’s contributions extend beyond clinical practice. She is a highly regarded author with an impressive portfolio of over 100 publications in prominent Indian, European, and American journals, with a specific focus on infertility. Her expertise is sought worldwide, as she serves as a respected speaker at international conferences and summits, including the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE).
Additionally, Dr. Dahiya plays a pivotal role as an advisor to numerous hospitals and serves as a mentor, training gynecologists aspiring to become proficient in reproductive medicine. Her extensive experience, exceptional knowledge, and dedication to her patients have solidified her reputation as one of the foremost experts in the field of infertility in India.