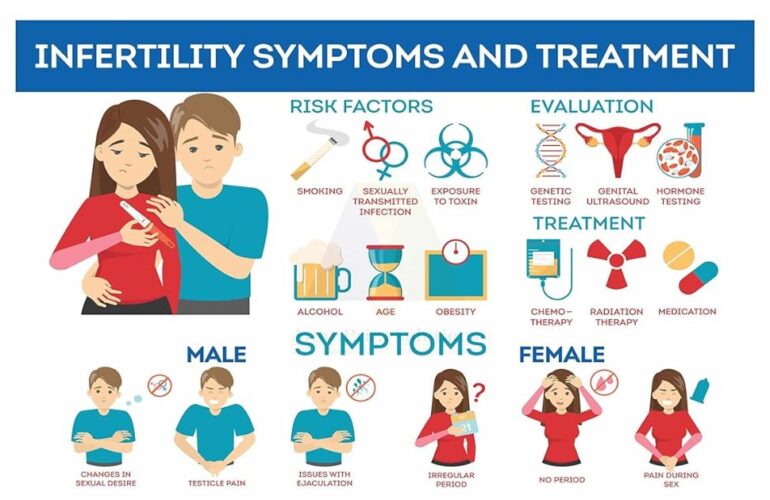
Infertility Overview
Medically, infertility is characterized as the inability to achieve pregnancy after one year of consistent, unprotected sexual activity. The European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology (EJOG) describes it as a disease of the reproductive system, which affects approximately 8-12% of couples worldwide. It is a condition that can be attributed to both men and women equally, challenging previous misconceptions that placed the burden primarily on females. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) and the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) emphasize the importance of recognizing infertility as a public health issue, which has profound psychological, economic, and medical implications. Despite its high prevalence, discussions around infertility are often clouded by stigma and lack of awareness, especially in developing nations.
According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), infertility rates are on the rise in India, with estimates suggesting that 14-15 million couples are affected. The importance of addressing infertility is underscored by its impact on the well-being of individuals and couples, influencing their mental health, social status, and overall quality of life. The purpose of my article is to give clarity about infertility, its biological roots, possible causes ranging from genetic anomalies to lifestyle factors and the diagnostic procedures available. Infertility Treatment can span from medication to Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF).
The Biology of Fertility
The reproductive system in both males and females is intricately designed for the purpose of procreation. In females, this system comprises the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina, while in males, it includes the testes, seminal vesicles, prostate, and penis. The ovaries produce eggs (ova) that travel through the fallopian tubes, where fertilization by sperm—produced by the testes—can occur. A fertilized egg then implants itself in the uterus to develop into a fetus.
Conception is a complex process that begins with ovulation, the release of an egg from the ovary. During intercourse, millions of sperm embark on a journey towards the egg, but only one typically penetrates the egg to achieve fertilization. According to “Human Reproductive Biology” by Richard E. Jones and Kristin H. Lopez, the likelihood of conception in any given menstrual cycle is just 20-25%.
Common biological causes of infertility include ovulatory disorders in women, which account for about 25% of all infertility cases as per the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Tubal blockages and uterine abnormalities are also significant factors. In men, infertility is primarily due to low sperm count or motility, contributing to approximately 40% of cases according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Factors like varicoceles affect about 15% of men, as reported in the journal “Fertility and Sterility”.
Other contributing conditions like endometriosis or genetic abnormalities are also notable causes. “Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine” highlights that endometriosis affects about 10% of women of reproductive age, significantly impacting fertility. These complexities underline the myriad of factors that can impede the path to pregnancy, reflecting the need for comprehensive evaluations and personalized treatments in the management of infertility.
Causes of Female Infertility
- Infertility in women: Infertility affects millions of couples worldwide, and understanding its causes is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Four common causes of infertility in women are ovulatory disorders, tubal damage, or blockage, uterine or cervical abnormalities, and endometriosis. These conditions contribute significantly to the challenges faced by those trying to conceive.
- Ovulatory Disorders: Ovulatory disorders are among the most common causes of infertility, accounting for about 25% of all cases of infertility. According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, ovulatory disorders involve irregular or absent ovulation, which is critical for conception. The most common type of ovulatory disorder is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), characterized by hormonal imbalances that interfere with the development and release of eggs. Other factors like excessive exercise, eating disorders, or obesity can also disrupt ovulation.
- Tubal Damage or Blockage: Tubal damage or blockage, typically resulting from inflammatory diseases like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), accounts for about 20-25% of infertility cases. These statistics are highlighted in ‘Infertility in the Modern World: Present and Future Prospects’ (Cambridge University Press). Fallopian tubes can become blocked or damaged due to infections, endometriosis, or previous surgeries, which prevents the egg from traveling down the tube to meet the sperm.
- Uterine or Cervical Abnormalities: Uterine or cervical abnormalities contribute to infertility in approximately 10% of cases, as noted in ‘Textbook of Assisted Reproductive Techniques’ by David K. Gardner. These abnormalities include congenital anomalies, polyps, fibroids, or adhesions that can interfere with the implantation of the fertilized egg or increase the likelihood of a miscarriage. Cervical factors might involve a physical blockage, hormonal imbalances, or issues with cervical mucus.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis affects roughly 10% of women of reproductive age, and it is a significant factor in infertility, as discussed in the ‘Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility’ by Marc A. Fritz and Leon Speroff. It occurs when the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows outside of it, often affecting the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the tissue lining the pelvis. This abnormal growth can cause pain, irregular bleeding, and, notably, difficulties in getting pregnant.
These conditions highlight the complexity of female reproductive health and the myriad factors that can impact fertility. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital in managing these conditions effectively. Advances in medical technology and treatments offer hope to many couples facing infertility due to these causes, though the journey can be challenging both emotionally and physically.
Causes of Male Infertility
- Infertility in men: Infertility is not just a woman’s issue; male infertility plays a significant role in about half of all cases where couples have difficulty conceiving. Understanding the various causes of male infertility is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Key factors include low sperm production, abnormal sperm function or blockages, varicocele, and lifestyle and environmental factors.
- Low Sperm Production: One of the most common causes of male infertility is low sperm production. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 15% of men have low sperm counts, which is less than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen. Low sperm production can result from genetic causes, hormonal disorders, testicular injuries, or infections such as mumps. In “Male Infertility: Problems and Solutions,” Edmund Sabanegh discusses how conditions like varicocele or previous surgeries can also impact sperm production.
- Abnormal Sperm Function or Blockages: Abnormal sperm function or blockages that prevent sperm delivery account for a significant portion of male infertility cases. Abnormal sperm function can include issues with the shape (morphology) and movement (motility) of the sperm, affecting its ability to reach and fertilize an egg. Blockages in the reproductive tract, which can be congenital or caused by infections and surgeries, can prevent sperm from being ejaculated. These issues are central in “Andrology: Male Reproductive Health and Dysfunction” by E. Nieschlag, et al.
- Varicocele: Varicocele, a swelling of the veins that drain the testicle, is found in about 15% of the general male population and up to 40% of men evaluated for infertility, as noted in “Campbell-Walsh Urology.” It can decrease sperm production and quality by affecting the temperature regulation of the testes and causing blood to pool.
- Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: Lifestyle and environmental factors significantly impact male fertility. These include exposure to certain chemicals and toxins, excessive alcohol and tobacco use, drug abuse, obesity, and certain medications. Stress and overheating of the testicles due to tight clothing or frequent use of hot tubs can also affect sperm production. These factors are highlighted in “Infertility in the Male” by Larry I. Lipshultz and Stuart S. Howards.
Understanding these factors is vital in addressing male infertility. With advancements in medical science, many causes of male infertility can be effectively treated, offering hope to many couples. Lifestyle modifications and treatments ranging from medication to surgical intervention can significantly improve the chances of conception.
Unexplained infertility:
Unexplained infertility affects approximately 15-30% of couples struggling with infertility. It is diagnosed when routine fertility tests – including semen analysis, ovulation assessment, and tubal patency tests – return normal results, yet conception remains elusive. This diagnosis, as detailed in “Infertility Counseling: A Comprehensive Handbook for Clinicians” by Sharon N. Covington, points to a gap in our understanding of the intricate process of conception. The challenge with unexplained infertility lies in its ambiguous nature. Without a clear cause, developing a targeted treatment plan becomes difficult. However, options like timed intercourse, ovarian stimulation, and assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) are often considered. Research, as discussed in “Clinical Gynecologic Endocrinology and Infertility” by Marc A. Fritz and Leon Speroff, suggests that factors such as subtle hormonal or immunological issues may play a role, though these are not well-understood.
Couples facing unexplained infertility need the counseling of an expert infertility specialist who have the experience to diagnose this uncertainty.
Diagnosis of Infertility
- Medical history and physical examination: The diagnosis of infertility often begins with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination, a crucial first step in identifying potential underlying causes. During the medical history, healthcare providers inquire about menstrual cycle regularity, past pregnancies, sexually transmitted infections, surgeries, and overall health, as well as lifestyle factors such as stress, diet, and exercise habits. The physical examination typically includes a general health check and specific reproductive system evaluation. For men, this might involve a testicular exam, while women may undergo a pelvic exam. This initial assessment, as highlighted in “Infertility in the Modern World” by Gillian R. Bentley, is fundamental in guiding subsequent, more specific fertility tests and treatments.
Infertility Tests for Women
In diagnosing female infertility, various tests are used to pinpoint the underlying problems. These tests range from tracking ovulation to more advanced imaging techniques. The associated costs of these procedures can vary, especially in India, where factors like location, facility, and specific technologies used play a role.
- Ovulation Tracking: Ovulation tracking is often the first step in assessing a woman’s fertility. This can be done through over-the-counter ovulation predictor kits, tracking menstrual cycles, or blood tests to check hormone levels. The cost of ovulation predictor kits in India ranges from INR 500 to 1,000 (approximately $2.50 to $13 USD).
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): Hysterosalpingography is a radiographic technique used to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes. It involves the injection of a contrast dye followed by X-rays. HSG is pivotal in identifying uterine abnormalities, scarring, or blockages in the fallopian tubes. In India, the cost of an HSG test typically ranges from INR 3,000 to 6,000 ($38 to $76 USD).
- Hormone Level Tests: Hormone tests are essential for evaluating fertility. They include measuring levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), prolactin, and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). These tests are crucial for assessing ovulatory function and general reproductive health. The cost for a comprehensive hormone panel in India can range from INR 500 to 1,000 ($19 to $51 USD), depending on the number and type of hormones tested.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests such as ultrasound are used to visualize the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. Transvaginal ultrasounds provide detailed images and are often used to monitor follicle development and check for abnormalities such as fibroids or polycystic ovaries. An ultrasound can cost between INR 600 to 1,000 ($13 to $32 USD) in India. More advanced imaging tests like Sono hysterography or MRI may be recommended in specific cases, which can significantly increase the cost.
The pricing data reflects a general range and can vary based on the reputation of the medical facility, and the specific technologies used. It is also important to note that these tests may be part of a more comprehensive infertility workup, and additional costs for consultation, follow-up, and potential treatments should be considered. These diagnostic tools are critical in formulating an effective treatment plan and offer valuable insights into a woman’s reproductive health.
Infertility Tests for Men
In the evaluation of male infertility, specific tests are crucial in determining the underlying causes. These tests range from basic semen analysis to more complex procedures like testicular biopsy. The costs for these tests in India can vary based on location, facility standards, and the specific nature of the test.
- Semen Analysis: Semen analysis is the cornerstone of male infertility testing. It assesses sperm count, morphology (shape), motility (movement), and volume. A standard semen analysis in India typically costs between INR 500 to 1,500 ($6 to $19 USD). This test can reveal issues like azoospermia (no sperm in the semen) and oligospermia (low sperm count), which are found in approximately 10-15% and 15-20% of infertile men, respectively.
- Hormone Testing: Hormone testing in men typically focuses on testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and prolactin. Hormonal imbalances can affect sperm production and sexual function. In India, the cost for a basic hormone panel can range from INR 1,000 to 3,000 ($13 to $38 USD). These tests are particularly important if semen analysis results are abnormal, as they can indicate issues with the pituitary gland or hypothalamus.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing may be recommended if there is a suspicion of genetic causes of infertility, such as Klinefelter syndrome or Y chromosome microdeletions. These conditions are relatively rare, affecting about 5% of infertile men. The cost for genetic testing in India is relatively higher due to its complexity, ranging from INR 10,000 to 15,000 ($127 to $382 USD).
- Testicular Biopsy: A testicular biopsy is performed when semen analysis shows very low or no sperm and is aimed at determining whether sperm production is occurring within the testes. This invasive procedure is less common and is usually considered when other tests fail to pinpoint the cause of infertility. In India, the cost for a testicular biopsy can vary widely, ranging from INR 25,000 to 30,000 ($191 to $637 USD), depending on the clinic and the type of anesthesia used.
The costs outlined provide a general idea, but actual prices may vary based on a Clinic’s Pricing strategy. These diagnostic tools are instrumental in guiding the appropriate course of treatment for male infertility and can provide crucial information about a man’s reproductive health.
Treatment Options for Infertility
Fertility drugs to stimulate ovulation:
Fertility drugs to stimulate ovulation are commonly used in treating women with ovulatory disorders. These drugs are available in both pill and injectable forms and invariably require a prescription, underscoring the importance of medical supervision during their use.
One widely used oral medication is Clomiphene Citrate, which stimulates ovulation by encouraging the pituitary gland to release more FSH and LH. The cost of Clomiphene in India ranges approximately from INR 350 to 500 ($4 to $6 USD) per cycle. Injectable hormones like Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Human Menopausal Gonadotropin (hMG) are more potent and typically used in cases where Clomiphene is ineffective. These can cost between INR 5,000 to 15,000 ($60 to $200 USD) per cycle in India.
Side effects can vary. Clomiphene may cause mood swings, headaches, and hot flashes, while injectables can lead to a higher risk of multiple pregnancies and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Regular monitoring by a fertility doctor is crucial to manage these risks effectively.
Surgical procedures:
Surgical procedures play a pivotal role in addressing specific physical causes of infertility, such as blocked fallopian tubes or varicocele.
- Tubal Surgeries: Tubal surgeries are often performed to repair or open blocked fallopian tubes, thereby enhancing the chances of natural conception. These procedures can vary in complexity and duration, typically taking about 1-3 hours. Laparoscopic surgery, a minimally invasive approach, is commonly used, leading to shorter recovery times of about 2-3 weeks. In India, the cost of tubal surgery can range from INR 50,000 to 60,000 ($375 to $750 USD), depending on the complexity of the procedure and the hospital.
- Varicocele Repair: Varicocele repair is aimed at sealing off the affected veins to redirect the blood flow into normal veins. This surgery, which can take about 2 hours, is often done on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day. Recovery typically takes about 2-3 weeks. In India, the cost for varicocele repair ranges from INR 30,000 to 50,000 ($380 to $625 USD).
Both types of surgeries have shown effectiveness in improving fertility outcomes. However, success rates can vary based on individual factors like age, underlying health issues, and the extent of the anatomical problem. Post-surgery, couples may be advised to wait for a few months before attempting conception to allow for complete healing and recovery.
Assisted reproductive technology (ART):
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) has revolutionized fertility treatment, offering hope to many couples struggling with infertility. The most common ART procedures include In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Intrauterine Insemination (IUI), and Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) and Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT).
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF involves stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, retrieving these eggs, fertilizing them with sperm in a lab, and then implanting the embryos into the uterus. The entire IVF cycle, from ovarian stimulation to embryo transfer, typically takes about 3 to 4 weeks. Post-embryo transfer, patients can usually resume normal activities within a few days. In India, the cost of an IVF cycle ranges from INR 1,00,000 to 2,00,000 ($1,250 to $2,500 USD), varying with the complexity of the case and additional treatments like ICSI.
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): IUI is a less invasive ART procedure where sperm are placed directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation. The IUI procedure itself takes only a few minutes and requires no recovery time, allowing patients to resume normal activities immediately. The cost per IUI cycle in India ranges from INR 10,000 to 15,000 ($125 to $200 USD).
- Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT) and Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT): GIFT and ZIFT are less common and involve transferring gametes (GIFT) or zygotes (ZIFT) directly into the fallopian tubes. These procedures require laparoscopic surgery, and the recovery time can be a few days to a week. They are typically used when there are unexplained infertility issues or problems with the fallopian tubes. The cost of GIFT and ZIFT in India ranges from INR 1,50,000 to 2,50,000 ($1,900 to $3,200 USD).
The choice of ART procedure depends on several factors, including the cause of infertility, age, and personal preferences. It is important to consult with a fertility specialist to understand the most appropriate treatment option. While these procedures offer hope, they also come with physical, emotional, and financial considerations that couples need to be prepared for.
Third-party assistance:
Third-party assistance in fertility treatments and alternative therapies have become increasingly significant options for couples facing infertility. These include egg and sperm donation, surrogacy, as well as alternative and complementary therapies.
- Egg Donation: Egg donation involves a donor providing eggs to be used for IVF. The process includes screening the donor, synchronizing cycles, stimulating the donor’s ovaries, and retrieving the eggs. The recipient undergoes hormonal treatments before the embryo transfer. The entire process can take several weeks. In India, the cost of an IVF cycle with donor eggs ranges from INR 1,50,000 to 2,50,000 ($1,900 to $3,200 USD). Donors typically recover from the egg retrieval procedure in a few days.
- Sperm Donation: Sperm donation is relatively simpler. Both IUI (Intrauterine Insemination) and IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) treatments can utilize donor sperm. The cost of IUI with donor sperm in India is around INR 15,000 to 20,000 ($190 to $250 USD) per cycle. For IVF, the cost ranges from INR 1,50,000 to INR 2,00,000 ($1900 USD To $2500 USD)
- Surrogacy: Surrogacy involves another woman carrying and giving birth to a child for the couple. It is a complex legal and medical process that can take several months to arrange and complete. Surrogacy in India is legally restricted and only available to Indian citizens. The “Surrogacy (Regulation) Act, 2021” serves as the detailed legal structure that regulates surrogacy practices in India. Enacted in 2021, it regulates various aspects of surrogacy procedures, including definitions, eligibility criteria, and the prohibition of commercial surrogacy. This legislation aims to ensure ethical and transparent surrogacy practices while safeguarding the interests of all parties involved. The costs, including medical and legal fees, can range from INR 10,00,000 to 15,00,000 ($12,500 to $19,000 USD).
Alternative and Complementary Therapies:
These include acupuncture, herbal treatments, yoga, and dietary strategies. While the efficacy of these treatments varies, they are often sought for their potential to improve overall fertility health. The cost and duration of these therapies can widely vary. For instance, a session in India might cost anywhere from INR 1,000 to 3,000 ($13 to $38 USD).
The choice of third-party reproductive assistance or alternative therapies should be made after thorough consultation with fertility specialists and considering legal, ethical, and emotional aspects. Recovery times and costs can vary based on individual circumstances and the specific nature of the treatment.
Resources And References
Organizations and support groups for infertility:
In India and Globally, several organizations and support groups aid and resources to individuals and couples dealing with infertility. Here are some notable organizations and support groups for infertility in India, USA, and UK.
- Fertility Preservation Society (FPS): FPS is a non-profit organization that aims to raise awareness about fertility preservation options and provides support to cancer patients and others facing fertility challenges.
- Indian Society for Assisted Reproduction (ISAR): ISAR is a professional organization in India that promotes and advances the field of assisted reproduction. They offer education and resources for both healthcare professionals and patients.
- Infertility Dost: Infertility Dost is an online platform and community that connects individuals and couples dealing with infertility. They offer support groups, webinars, and a wealth of information on infertility-related topics.
- Fertility Matters India: This organization focuses on raising awareness about infertility and providing support to those affected by it. They offer online forums, counseling services, and educational resources.
- SNEHIKA – Support Group for Women with Infertility: SNEHIKA is a support group for women dealing with infertility in India. They provide a safe space for sharing experiences and seeking emotional support.
- RESOLVE: The National Infertility Association: RESOLVE is a leading nonprofit organization in the United States dedicated to supporting those struggling with infertility. They offer educational resources, support groups, advocacy, and a helpline.
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM): ASRM is a professional organization that provides information on reproductive health and infertility treatment options. They offer patient education materials and a directory of fertility specialists.
- Fertility Network (UK): This UK-based charity offers support and information to individuals and couples dealing with fertility challenges. They provide support groups, a helpline, and educational resources.
- Path2Parenthood: Formerly known as the American Fertility Association, this organization offers support and education on reproductive health and family-building options. They have a variety of resources and programs for individuals and couples.
- Resolve Through Sharing (RTS): RTS is a support organization that focuses on pregnancy loss, stillbirth, and reproductive grief. They offer resources and training for healthcare professionals and support for individuals and families.
These organizations and support groups in play a crucial role in helping individuals and couples navigate the challenges of infertility. They offer a range of services, from emotional support and counseling to educational resources. They ultimately help people to make informed decisions and find the support they need.
Books and articles for Infertility:
- “Taking Charge of Your Fertility” by Toni Weschler: This book provides valuable insights into understanding one’s menstrual cycle and optimizing fertility.
- “It Starts with the Egg” by Rebecca Fett: This book explores the role of egg quality in fertility and offers strategies to improve it.
- “The Infertility Cure” by Randine Lewis: Dr. Randine Lewis discusses traditional Chinese medicine approaches to treating infertility.
- “The Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics” (Journal): This scientific journal publishes articles on various aspects of assisted reproductive technology and infertility research.
World Famous Clinics for Infertility Treatment:
- Mayo Clinic Fertility Center (USA): The Mayo Clinic offers comprehensive fertility services, including diagnosis and treatment, with a focus on patient-centered care.
- Shady Grove Fertility (USA): Known for its high success rates, Shady Grove Fertility is one of the largest fertility centers in the United States.
- LWC Fertility (UK): The London Women’s Clinic provides a range of fertility treatments and has a strong reputation for patient care.
- Monash IVF (Australia): Monash IVF is a leading fertility clinic in Australia, offering a wide range of services and treatments.
- Little Angel IVF (India): The clinic offers a comprehensive range of fertility services like IVF, ICSI, Fertility Preservation and boasts of the Highest Success Rate Globally.
FAQ’S
Q1. What defines infertility?
Infertility is typically described as the inability to achieve pregnancy after one year or more of regular, unprotected intercourse.
Q2. What causes infertility?
Infertility is described as the incapacity to achieve pregnancy after one year of regular attempts to conceive. This condition can be due to various factors like issues with ovulation, endometriosis, insufficient sperm count, or low testosterone levels. Additionally, the likelihood of experiencing infertility typically rises with advancing age.
Q3. What is female infertility?
Female infertility is the inability of a woman to conceive after a year of regular, unprotected intercourse. It can result from various issues, including hormonal imbalances, ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, or uterine abnormalities, and becomes more common as a woman ages.
Q4. Can infertility be cured?
The approach to fertility treatment is tailored to everyone, considering factors like the underlying cause of infertility, age, and any additional health concerns. Although there is no universal cure for infertility, numerous effective strategies are available to address and manage it.
Q5. Can masturbation cause low sperm count?
Regular male masturbation is generally not considered to significantly impact fertility. Studies indicate that the best semen quality is often seen after a period of two to three days without ejaculation. However, additional research points out that men with normal sperm quality can still maintain healthy sperm movement and concentration, even with daily ejaculation.
Q6. What are the Fertility tests for women?
- Ovulation Testing: Blood tests to check hormone levels or over-the-counter ovulation kits.
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): An X-ray to evaluate the uterus and fallopian tubes for blockages or other issues.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Imaging to assess the ovaries, uterine lining, and uterus structure.
- Hormone Testing: Blood tests to measure levels of ovarian, pituitary, and thyroid hormones.
- Ovarian Reserve Testing: Tests, often involving blood tests and an ultrasound, to determine the quantity and quality of eggs available for ovulation.
- Endometrial Biopsy: Examining the lining of the uterus to check for abnormalities.
- Genetic Testing: To identify any genetic abnormalities that might affect fertility.
Q7. Is infertility permanent?
Infertility is not always permanent. Many cases can be treated successfully with medical interventions, lifestyle changes, or assisted reproductive technologies. The prospects for reversing infertility depend on the underlying cause and factors like age and overall health.
Q8. Who is at risk of infertility?
Individuals at risk of infertility include those with a history of sexually transmitted infections, hormonal imbalances, genetic disorders, age-related factors, and lifestyle choices like smoking or excessive alcohol use. Both men and women can be equally affected by fertility issues.
Q9. How can I check my fertility at home?
To check fertility at home, women can use ovulation predictor kits to track ovulation, while men can use at-home semen analysis kits. Monitoring menstrual cycles and overall health signs can also provide insights into fertility status.
Q10. How to avoid infertility?
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight can enhance fertility.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are linked to reduced fertility in both men and women.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect hormonal balance and ovulation. Practices such as yoga, meditation, and seeking counseling can offer significant benefits.
- Limit Exposure to Toxins: Avoid exposure to environmental and occupational toxins, including certain pesticides and chemicals.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Regular health screenings can help detect and manage conditions that might affect fertility, such as STIs, hormonal imbalances, or other health issues.
Q11. Can I check if I am infertile?
Yes, you can check if you are infertile through medical evaluations. For women, this includes hormone testing, ovulation tracking, and pelvic exams. For men, semen analysis is key. Consulting a Fertility Doctor is essential for accurate assessment and guidance.
Q12. Do heavy periods affect fertility?
If you experience regular menstrual cycles but are struggling to conceive, aspects such as the length of your cycle and the heaviness of your menstrual flow can influence your fertility. This is because the hormones that control your menstrual cycle, aid in conception, and sustain a pregnancy, also affect your periods. Heavy periods can affect fertility, often indicating underlying conditions like fibroids, polyps, or hormonal imbalances, which can impact ovulation and the uterine environment.
Q13. What is the age limit for infertility?
There is no strict age limit for infertility, but fertility naturally declines with age. Women’s fertility typically decreases more significantly after age 35, while men may experience a gradual decline in fertility after age 40. However, individual cases can vary widely.
Q14. How can I become fertile naturally?
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being either underweight or overweight can affect hormone levels and ovulation.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support reproductive health.
- Exercise Regularly: Moderate, regular exercise can boost fertility, but excessive exercise might have the opposite effect.
- Reduce Stress: High stress levels can disrupt menstrual cycles and ovulation, so finding effective stress-reduction techniques is important.
- Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and heavy alcohol consumption can decrease fertility in both men and women.
Q15. Is IVF legal in India?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is legal in India and widely practiced, with numerous specialized clinics across the country. However, the Indian government regulates certain aspects, such as surrogacy and egg donation, to ensure ethical practices in assisted reproductive technologies.
Q16. Which fruit is best for fertility?
Fruits rich in antioxidants like berries, citrus fruits, and bananas are considered beneficial for fertility. They contain vitamins and minerals like vitamin C, folate, and potassium, which can improve reproductive health by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the body.
Q17. Can unmarried woman donate her eggs?
Yes, an unmarried woman can donate her eggs. Egg donation typically does not require the donor to be married. However, donors must meet specific criteria related to age (Up to 28 Years), health, and psychological well-being, and undergo a thorough screening process.
Q18. Which drink is best for conceiving?
Drinks that are beneficial for conceiving include water to maintain hydration, pomegranate juice for antioxidants, and whole milk or milk alternatives rich in calcium and vitamin D. Limiting caffeine and avoiding alcohol are also advised for optimal fertility.
Q19. Is marriage certificate required for IVF in India?
In India, a marriage certificate is not legally required for IVF treatment. However, individual clinics may have their own policies for Proof of Relationship like Aadhar Card or Passport.
Q20. What is difference between fertility and infertility?
Fertility refers to the natural capability to conceive a child, indicating healthy reproductive systems in both men and women. Infertility, on the other hand, is the inability to conceive after a year or more of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse, often due to underlying health issues affecting the reproductive system.
Q21. How do I know if I am infertile female?
Infertility is identified when you are under 35 and unable to conceive after a year of trying, or over 35 and have not succeeded in getting pregnant after six months. It is also considered if you have experienced two or more miscarriages or have not had success with other fertility treatments.
Q22. Is 37 too late for IVF?
At 37, IVF is still a viable option with success rate of about 60%. While fertility declines with age, many women at 37 successfully undergo IVF. Success rates vary and consulting with a fertility specialist can provide a clear understanding of individual chances and any additional considerations.
Q23. Is 45 too late for IVF?
While IVF is possible at 45, success rates are lower due to decreased fertility. Women over 40 face lower success rates like 25%, with those above 45 having only about a 10% chance of a successful live birth through IVF. Additionally, pregnancy at an older age carries increased risks of complications.